Table of Contents
- 1. What Are Surgical Staples?
- 2. Benefits of Surgical Staples Over Sutures
- 3. Applications of Surgical Staples
- 4. How to Use Surgical Staples Safely
- 5. How to Remove Surgical Staples
- 6. Surgical Staples vs. Surgical Skin Staplers
- 7. Why Choose Surgical Staples Over Traditional Methods?
- 8. FAQs About Surgical Staples
- 9. Conclusion
Surgical staples have revolutionized wound closure in modern medicine, offering efficiency and precision for a variety of procedures. From external skin closures to complex internal surgeries, these staples play a crucial role in the healing process. This comprehensive guide explores what surgical staples are, their benefits, applications, and essential tips for their use and removal.
What Are Surgical Staples?
Surgical staples are specialized medical devices used to close wounds or surgical incisions. Unlike traditional sutures, staples are metal or plastic fasteners that ensure a strong and uniform closure. They are commonly made from stainless steel, titanium, or other biocompatible materials, minimizing the risk of infection or adverse reactions.
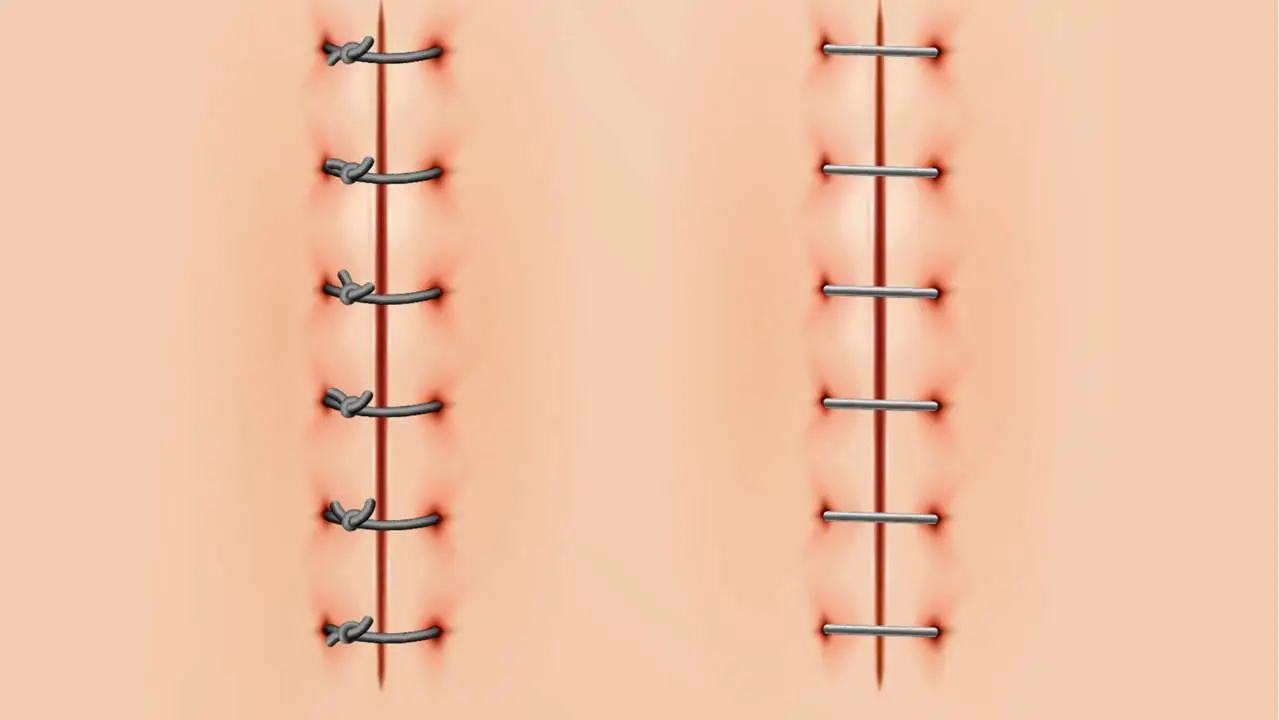
Types of Surgical Staples
- Skin Staples: Designed for external closures.
- Internal Staples: Used for organ or tissue reconnection, such as bowel resections.
- Disposable vs. Reusable: Disposable staples are preloaded in a stapler, while reusable ones require sterilization.
The metals that most commonly make up surgical staples include titanium and stainless steel. However, other materials that sometimes make up surgical staples can include:
- iron
- chromium
- nickel
- plastic
Surgical staples may be different shapes, including:
- straight
- curved
- circular
Benefits of Surgical Staples Over Sutures
- Speed: Staples allow for quicker wound closure, especially in large or complex incisions.
- Consistency: They provide even tension along the wound, reducing the risk of uneven healing.
- Reduced Scarring: Properly applied staples can minimize scarring compared to poorly executed sutures.
- Versatility: Staples are suitable for various procedures, including trauma care, abdominal surgeries, and thoracic operations.
There was no significant difference between sutures and staples in:
• the development of inflammation
• discharge
• dehiscence (re-opening of a previously closed wound)
• necrosis
• allergic reaction
Applications of Surgical Staples
Common Uses
- Emergency Medicine: Quick closure of lacerations and open wounds.
- Surgical Procedures: Securing tissue during surgeries like bowel resections or lung surgeries.
- Veterinary Applications: Used in animal surgeries due to their efficiency and strength.
Who Should Use Surgical Staples?
- Medical Professionals: Surgeons, emergency room doctors, and trained medical staff are primary users.
- Veterinarians: Ideal for rapid wound closures in animals.
How to Use Surgical Staples Safely
- Preparation: Ensure the wound edges are clean and aligned.
- Application: Use a stapler device to gently compress the tissue and apply the staple.
- Inspection: Check for even spacing and proper closure to avoid complications.
Tips for Best Results
- Always use sterile equipment.
- Avoid over-tightening to prevent tissue damage.
- Use only on wounds suitable for staple closure.
A medical professional usually removes surgical staples around 10–12 days after the procedure. However, this can vary.
Several factors can affect how long the staples remain in the body, including:
- the size of the incision
- the direction of the incision
- the type of surgery
- the severity of the incision or wound
- the area of the body where the staples are present
- how quickly the wound heals
In some cases, surgical staples can offer wound closure 10 timesTrusted Source faster than sutures.
How to Remove Surgical Staples
Removing surgical staples requires a specialized staple remover. Follow these steps:
- Sterilize the Area: Clean the wound with an antiseptic solution.
- Use a Skin Staple Remover: Insert the device under the staple and gently squeeze to lift it.
- Inspect the Wound: Ensure no staples remain and the wound is healing properly.
Surgical Staples vs. Surgical Skin Staplers
Key Differences
- Surgical Staples: Refers to the staples themselves, used for both internal and external applications.
- Skin Staplers: Devices specifically designed to apply staples for external wound closure.
Why Medical Skin Staplers Are Popular
- Easy to use and cost-effective.
- Commonly used in outpatient procedures and emergency care.
Why Choose Surgical Staples Over Traditional Methods?
- Faster Procedure Times: Essential in emergency situations.
- Lower Infection Rates: Biocompatible materials reduce complications.
- Cost-Effective: Fewer materials and faster application reduce overall costs.
FAQs About Surgical Staples
Can I Use Surgical Staples for Veterinary Purposes?
Yes, surgical staples are widely used in veterinary medicine for quick and reliable wound closures in animals.
How Long Should Surgical Staples Stay In?
Typically, staples remain in place for 7-14 days, depending on the wound and its location. Consult a healthcare professional for specific guidance.
Are Surgical Staples Painful?
Patients may experience mild discomfort during removal, but the procedure is generally quick and well-tolerated.

Conclusion
Surgical staples are an invaluable tool in modern medicine, offering speed, efficiency, and reliability. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or a patient seeking information, understanding their applications, benefits, and proper use ensures optimal outcomes. If you have specific questions or concerns about surgical staples, consult a qualified medical professional for personalized advice.



